What if copyright law took authors rights seriously? Many groups claim to do so, but Professor Rebecca Giblin, one of the world’s leading experts on creator copyright, isn’t convinced. Professor Giblin argues that creators are often placed at the centre of the debate only to be largely ignored by other stakeholders. Professor Giblin joins this week’s Lawbytes podcast to talk about her Author’s Interest Project, the latest data, and why Canadian artist Bryan Adams may be on to something when it comes to his copyright reform proposal to benefit creators.
Fair Dealing by Giulia Forsythe (CC BY-NC-SA 2.0) https://flic.kr/p/dRkXwP
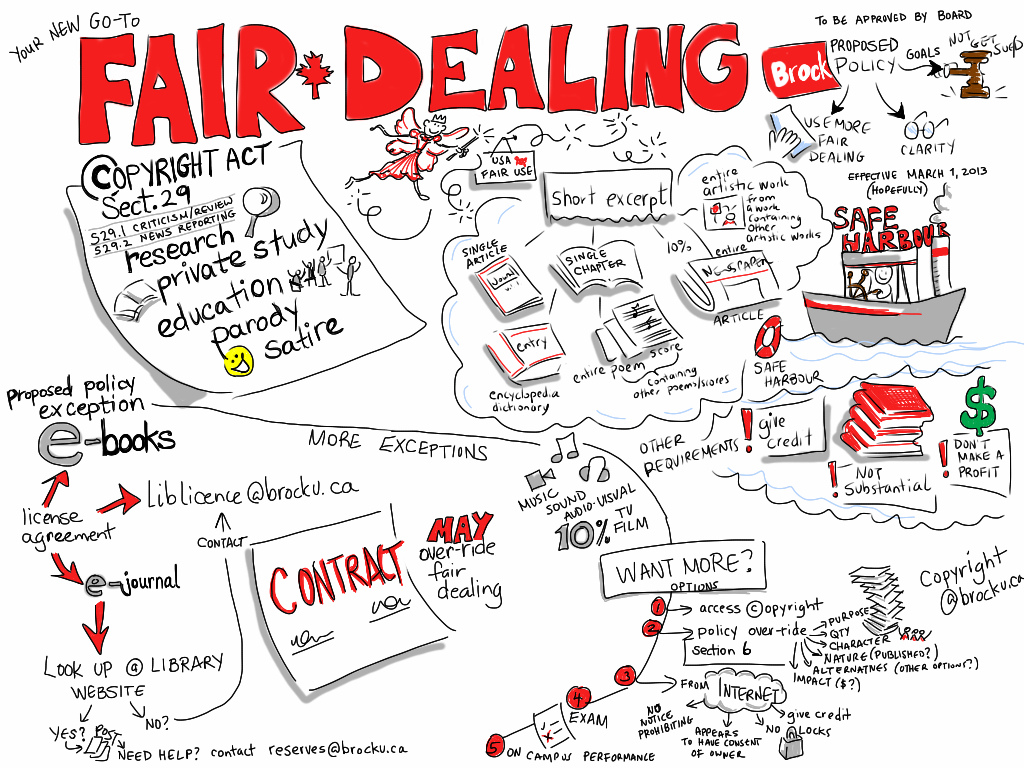
Copyright
The LawBytes Podcast, Episode 5: “A Huge Threat to How the Internet Functions Now”
Most treaties are negotiated behind closed doors with no text made available until after a deal has been reached. Yet there is a treaty with enormous implications for the Internet, copyright, and broadcasting that has been hidden in plain sight for the better part of two decades. This week, the World Intellectual Property Organization resumes discussions in Geneva on a proposed Broadcasting Treaty. To introduce WIPO, the proposed treaty, and its implications, Jamie Love of Knowledge Ecology International joins this week’s LawBytes podcast. Love warns that the treaty could extend the term of copyright for broadcast content, create a wedge between broadcasters and Internet streaming services, and even result in new restrictions on the use of streaming video.
The LawBytes Podcast, Episode 4: Going Inside Canada’s Copyright Review
The House of Commons Standing Committee on Industry, Science and Technology has spent the past year reviewing the state of Canadian copyright law. The review, which is scheduled to result in a report with recommendations for potential reforms, featured hundreds of witnesses representing a wide range of views. To introduce some of the issues and provide some insight into how the review process functions, this week’s LawBytes podcast relies on the audio recording of my committee appearance in December 2018. It opens with my seven minute opening statement and continues with several exchanges with MPs on issues such as fair use, the USMCA, crown copyright, and anti-circumvention rules, which are often referred to as digital locks.
How Canadian Copyright Reform Could Support the Government’s Supercluster Investment
The release of Budget 2019 yesterday again placed the government’s innovation strategy in the spotlight as the government emphasized its significant spending record, including $950 million for the superclusters, $4 billion for science research, $795 million in 31 strategic innovation fund agreements and $2.3 billion for clean technology support. The investments were highlighted in a recently released an innovation scorecard, Building a Nation of Innovators, which takes stock of the government’s efforts over the past three years. My new CIGI policy brief argues that while the benefits from this spending will take years to realize, increased investments in strategic sectors are the easy part of innovation policy.
Canada’s Internet Music Success Story: SOCAN’s Canadian Internet Streaming Revenues Surpass Radio Royalties
While the music industry continues to focus on a so-called “value gap” that does not reflect the state of Canadian law, mounting data also suggests that it does not provide an accurate depiction of the revenues being generated in Canada today from Internet streaming. SOCAN, Canada’s largest music copyright collective, last week reported preliminary numbers for 2018, with the data indicating that Internet streaming revenues have now hit $62 million, likely surpassing both radio and television royalties as its second largest source of domestic revenues. In fact, Internet streaming now accounts for 22 per cent of SOCAN’s domestic revenues and will almost certainly become its largest domestic revenue source in 2019.











