My recent series reviewing the Industry Committee’s copyright review (process, evidence, witness balance, citation) was about more that just why the decision to ignore the Canadian Heritage committee study on artist remuneration was justified. The series provides a data-backed assessment of the quality of the consultation of the respective committees, which is inextricably linked to their final recommendations. The better process is important because when comparing the recommendations from the two committees, the Industry committee consistently provided deeper analysis even in areas where there was agreement. The better analysis is not a coincidence: better process generates better policy and the Industry committee engaged in broader consultations in which it heard both from more creators and more users than Heritage.
News
Ignoring the Evidence: Why the Copyright Review Was Right To Ignore the Canadian Heritage Committee Study, Part Four
My series on why the Industry committee was right to ignore the Canadian Heritage committee study as part of the national copyright review has previously discussed process (the government vested sole responsibility with the Industry committee), an examination of the witness and brief list that confirms that Industry conducted a much more comprehensive consultation that overlapped with much of Heritage but also included hundreds of additional witnesses and briefs, and the (im)balance among witnesses which indicates that the Industry committee made a greater effort to hear a wide range of perspectives consistent with the diverse views on copyright.
Unbalanced Witness List: Why the Copyright Review Was Right To Ignore the Canadian Heritage Committee Study, Part Three
My series on why the Industry committee was right to ignore the Canadian Heritage committee study as part of the national copyright review has focused on process (the government vested sole responsibility with the Industry committee, its clear assertion as the authoritative copyright review, and an examination of the witness and brief list that confirms that Industry conducted a much more comprehensive consultation that overlapped with much of Heritage but also included hundreds of additional witnesses and briefs.
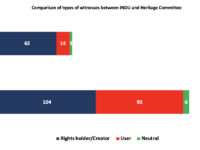
Limited Views: Why the Copyright Review Was Right To Ignore the Canadian Heritage Committee Study, Part Two
The Industry committee’s clear assertion this week as the authoritative copyright review is grounded in process since the government gave it sole responsibility for conducting the review. While my earlier posts focus on the process and the unprecedented INDU release, the committee justifiably points out that it also heard from far more witnesses through hearings and briefs than the Heritage committee. In fact, it notes that it heard from the “vast majority of stakeholders who contributed to CHPC’s study.” Working with University of Ottawa student Philip Abraham, we reviewed the witness lists, the brief submissions, and the citations by the committees to better assess claims about which committee best reflects the full spectrum of stakeholder views on copyright. This post examines who participated in the committee work and a follow-up posts will highlight the balance in the witness lists and whether the committees were listening.
“Sole Responsibility” for the Copyright Review: Industry Committee Issues Unprecedented News Release Confirming It Was Right To Ignore the Canadian Heritage Committee Study
My series on why the Industry committee rightly chose to ignore the Canadian Heritage committee study on artist remuneration took an unexpected turn yesterday. Hours after I posted an analysis demonstrating that the Heritage committee had ignored its mandate by tabling its report in the House of Commons, the Industry committee issued an unprecedented news release confirming that it did not consider the Heritage report and that its report is the exclusive copyright review. The news release states: