Last month, Liberal MP Lisa Hepfner shocked Canadian online news outlets by stating that “they’re not news.They’re not gathering news. They’re publishing opinion only.” The comments sparked instant criticism from news outlets across the country, leading Hepfner to issue a quick apology. In the aftermath of the comments, Hepfner said nothing for weeks at Heritage committee studying Bill C-18. That bill passed third reading yesterday – I posted on the embarrassing legislative review – and Hepfner was back at it. Rather than criticizing online news outlets, this time she targeted the Internet platforms, saying the bill would make it “harder for big digital platforms like Facebook and Google to steal local journalists’ articles and repost them without credit.”
Post Tagged with: "twitter"
The Bill C-18 Fallout: Liberal MP Lisa Hepfner Equates Linking to News Articles on Facebook to Theft
Age Verification Requirements for Twitter or Website Blocking for Reddit?: My Appearance on Bill S-210 at the Senate Standing Committee on Legal and Constitutional Affairs
Bill C-11, the government’s online streaming bill, is rightly garnering increasing attention, but there is a private member’s Senate bill that should also be on the radar screen. Bill S-210, a follow-up to S-203, is a bill that purports to restrict underage access to sexually explicit material. Sponsored by Senator Miville-Dechêne, a former CBC journalist appointed to the Senate in 2018, the bill would require age verification requirements for sites (likely backed by face recognition technologies) and mandated website blocking for sites that fail to comply with the verification requirements.
The LawBytes Podcast, Episode 54: Eric Goldman on Internet Platform Liability and the Trump Executive Order
The U.S. approach to Internet platform liability has been characterized as the single most important legal protection for free speech on the Internet. Over the past two decades, every major Internet service has turned to the rules to ensure that liability for third party content posted on their sites rests with the poster, not the site or service. Those rules have proven increasingly controversial, however, with mounting calls for the companies to take on greater responsibility for content posted on their sites. The issue captured international attention last month when U.S. President Donald Trump issued an Executive Order that heightens the pressure for change.
Eric Goldman is a Professor of Law at Santa Clara University School of Law in the Silicon Valley where he co-directs the High Tech Law Institute. He has written extensively about Internet liability and appeared before the US Congress to testify on the issue. He joins me on the podcast to discuss the history behind the U.S. approach, its impact, and the implications of the Trump Executive Order.
Why the USMCA Locks in the Internet Platform Liability System in the U.S., Canada and Mexico
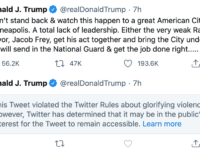
U.S. President Donald Trump yesterday signed an executive order targeting Internet platforms after Twitter fact-checked one of his tweets on mail-in voting (the company followed up with a warning on another tweet earlier today involving glorifying violence). The order cannot simply reverse current U.S. law, but it encourages U.S. regulators to rethink how the Internet safe harbour provisions that limit liability for Internet platforms for third party content are implemented.
While the U.S. is obviously free to assess its statutory approach, one issue that received little attention is that the U.S. has effectively locked itself into the safe harbour system through its trade agreement with Canada and Mexico. The inclusion of safe harbour provisions in the agreement were viewed by some as an attempt to force Canada to adopt similar rules, yet the more likely reason for lobbying on the issue was to ensure that the U.S. itself was bound by the rules. Indeed, there were last minute efforts to remove the provision from the final deal, but those were ultimately rejected.
Twitter Issues Transparency Report
Twitter has issued a transparency report that discloses government requests for user information along with copyright takedown demands. The report indicates that there were 11 Canadian user information requests in the first half of 2012, behind only the U.S. (easily the most requests) and Japan.