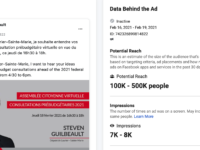
Canadian Heritage Minister Steven Guilbeault yesterday told the House of Commons Heritage Committee that his department would reduce the amount it allocates to digital advertising, arguing that too much goes to online platforms and that “we need to change this.” The decision to politicize where the government spends its ad dollars is perhaps unsurprising given Guilbeault’s penchant for battling with the tech companies, dating back to his claims that linking to news articles without payment is “immoral.” Leaving aside the question of whether taxpayer funded advertising campaigns should prioritize effectiveness and value for money (personally, I’d prefer that the government emphasize the effectiveness of ad campaigns on issues like COVID-19 vaccination and safe social distancing practices over political posturing even if that means advertising on digital platforms), the reality of Guilbeault’s own Facebook practices do not match up with his rhetoric.
 Articles by: Michael Geist
Articles by: Michael Geist
The Law Bytes Podcast, Episode 79: David Kaye on the Challenges of Reconciling Freedom of Expression and the Regulation of Online Harms
Canadian Heritage Minister Steven Guilbeault is expected to soon introduce new legislation designed to address online harms through increased regulation. Reports indicate that the bill will target five categories of illegal content: hate speech, terrorist content, content that incites violence, child sexual exploitative content and non-consensual sharing of intimate content. The details will matter, however, as failure to ensure due process for content removal and strict limits on scope will raise constitutionality concerns.
David Kaye is a clinical professor of law at the University of California, Irvine, and served as the United Nations Special Rapporteur on the promotion and protection of the right to freedom of opinion and expression from 2014 until 2020. He joins the Law Bytes podcast to discuss the challenges associated with balancing regulation and preserving freedom of expression online, the policy considerations that governments should be thinking about, and the risks that arise from getting the balance wrong.
Misplaced Priorities: Why Has Canada’s Privacy Bill Disappeared from the Government’s Legislative Agenda?
Last November, then Innovation, Science and Economic Development Minister Navdeep Bains introduced Bill C-11, long overdue privacy reform. The bill appeared to be a top government priority, with Prime Minister Justin Trudeau emphasizing that the new law would give Canadians more control over how companies handle their personal information. While the bill isn’t perfect – I wrote posts on some of the benefits and concerns – there was no debating that it represented an important step forward in modernizing Canada’s privacy law.
Yet months after the bill was introduced, it is seemingly going nowhere.
Is Bill C-10 Unconstitutional? A Former Justice Senior General Counsel Makes the Case It Is
As the Standing Committee on Canadian Heritage continues its study on Bill C-10, it has also received some notable submissions from organizations and experts that raise further questions about the wisdom of the bill. One submission not yet posted (but provided to me with the consent to post) comes from Philip Palmer, former Senior General Counsel with the Department of Justice focused on communications law. Palmer spent decades in government focused on telecommunications and competition law issues. His expert opinion is that Bill C-10 is unconstitutional since on-demand streaming services such as Netflix are not inter-provincial undertakings and therefore are not subject to the federal government’s jurisdiction over broadcasters.
The Law Bytes Podcast, Episode 78: Jennifer Jenkins on What Copyright Term Extension Could Mean for Canada
For years, Canada resisted extending the term of copyright beyond the international standard of life of the author plus 50 years. That appears to have come to an end with the USMCA, which requires an extension. The Canadian government has just launched a public consultation on the issue, identifying several “accompanying measures” to address concerns about the negative impact of term extension. For the many Canadians that participated in the recent copyright review process, the consultation document comes as huge disappointment as it seemingly rejects – with little legal basis – the review’s recommendation on establishing a registration requirement for the additional 20 years that would benefit both creators and the public.
The consultation is currently open until March 12th. Duke University’s Jennifer Jenkins, who is is a Clinical Professor of Law teaching intellectual property and Director of Duke’s Center for the Study of the Public Domain, joins the Law Bytes podcast this week to help sort through the likely implications of copyright term extension for Canada.