Bill C-18, the Online News Act, heads to clause-by-clause review this week at the Senate Transport and Communications Committee. The committee’s study of the bill wasn’t as extensive as Bill C-11, but it did hear from a very wide range of stakeholders and experts. Last month, I devoted the Law […]
Search Results for "c-11" : 409
Globe Publisher Calls Bill C-18 a “Threat to the Independence of Media” As Government Senate Representative Smears Bill Critics
The Senate hearings on Bill C-18, the Online News Act, resumed yesterday with two blockbuster panels that included the Globe and Mail, News Media Canada, La Presse, Le Devoir, Canadaland, The Line, and Village Media. The unmistakable takeaway was the enormous risks the bill creates to the independence of the press, to the future of digital media, and to the bottom lines of Canadian news outlets across the country. Further, it is increasingly apparent that the government has no real answers to these risks other than sabre rattling with tech companies and questioning the motives of critics of the legislation.
The eagerness to smear anyone who dares criticize the bill provided the most jaw-dropping moment of the hearing with Senator Peter Harder, the government’s representative in the Senate on the bill, suggesting that Bill C-18 criticism from Village Media’s Jeff Elgie, one of Canada’s most successful local digital news organizations, might be motivated by the business benefits of local media shutting down:
This Must Stop: Government and Liberal Party Go All-In On Speech Regulation With Political Truth Oversight Bodies, Mandated Press Source Tracing, and Disclosure of Critics’ Communications
Earlier today, the Liberal party convention approved (subject to a final vote) two stunning policy resolutions with enormous implications for freedom of expression. First, as discussed yesterday, it approved a resolution that seeks to “hold on-line information services accountable for the veracity of material published on their platforms and to limit publication only to material whose sources can be traced.” If enacted, the policy would undermine freedom of the press and could even spark widespread censorship on Internet platforms. In addition, it passed a resolution to develop “truth in political advertising” legislation to be administered by an oversight body. There are legitimate concerns about the “truthiness” of all political parties communications, but political truth oversight bodies carries great risk and is unlikely to foster enhanced public trust.
Why the Twitter – CBC Labelling Battle is a Distraction From the Real Problems with Government Media Policy and the Public Broadcaster
Twitter and the CBC were in the spotlight yesterday with Twitter’s decision to add a “government funded media” label to the CBC Twitter account. The label is defined by Twitter as a media organization “where the government provides some or all of the outlet’s funding and may have varying degrees of government involvement over editorial content.” CBC responded by tweeting it would pause its Twitter activities because suggesting that its journalism was anything other than impartial and independent was untrue. The government funding for CBC is undeniable, but the inclusion of “government involvement over editorial content” is apt to mislead. The Broadcasting Act provides guidance on the kinds of content to be found on CBC, but there is an important difference between general policy objectives and specific involvement over editorial content. In fact, Twitter has another label for “publicly funded media” accounts that appear to be better suited to the CBC since it covers “media organizations that receive funding from license fees, individual contributions, public financing, and commercial financing” but makes no reference to editorial content.
The Twitter-CBC labelling battle offers more heat than light since it does little to address the underlying problems with media independence in Canada and the CBC (much less the tire fire that is Twitter). Instead, it simply provides fodder for CBC critics to point to the Twitter label and argue for “defunding the CBC” (at least the English language part of it) and CBC defenders to proclaim that they will stand up for the public broadcaster against unfair smears. That debate distracts from serious underlying problems with government media policy and the public broadcaster.
Government Departments Pressure Social Media Sites to Censor News Links, Mean Tweets
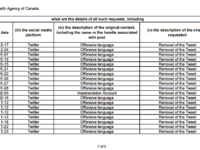
The risks associated with the government’s online harms (or online safety) plans is not limited to Canadian Heritage’s credibility gap, which as I’ve recounted has included omitting key information in its public reports on consultations and shocking efforts to exclude contrary voices altogether. A new report, based on the government’s response to a Parliamentary Written Question from Conservative MP Dean Allison (Sessional Paper No. 8555-441-1219) raises new concerns about efforts to censor social media. The written question asked the government for “requests made by the government to social media companies to take down, edit, ban or change in any other way social media content, posts or accounts since January 1, 2020.”
The resulting report is stunning as government departments have in fact pressured the social media companies to remove news links and a range of lawful content including tweets that are said to contain “offensive language” or an “offensive reply.” The use of government power to censor social media posts or news links is exceptionally dangerous and crystallizes the fears of regulatory powers without the necessary due process and oversight that could lead to censorship of lawful content online.