Last week, the European Commission launched what promises to be a global, multi-year debate on the regulation of artificial intelligence. Several years in development, the proposed rules would ban some uses of AI, regulate others, and establish significant penalties for those that fail to abide by the rules. European leaders believe the initiative will place them at the forefront of AI, borrowing from the data protection framework of seeking to export EU solutions to the rest of the world. Céline Castets-Renard is a colleague at the University of Ottawa, where she holds the University Research Chair on Accountable Artificial Intelligence in a Global World. She joins the Law Bytes podcast to discuss the EU plans, their implications for Canadian AI policy, and the road ahead for the regulation of artificial intelligence.
Post Tagged with: "EU"
The Broadcasting Act Blunder, Day 19: The Misleading Comparison to the European Union
The Broadcasting Act blunder series has featured several posts raising concerns that Bill C-10 is likely to increase costs for consumers and decrease choice as some services block the Canadian market altogether. Canadian Heritage Minister Steven Guilbeault has regularly cited the situation in Europe as evidence that the concerns are unfounded. For example, he told the House of Commons that “European Union has adopted new rules on streamers resulting in increased investment, jobs, choice of content and ability to assert one’s own cultural sovereignty” and told the media that the European Union has had a requirement since 2018 that 30% of Internet streaming services content must be European content without resulting in higher fees.
Guilbeault’s comparison of Bill C-10 to the situation in Europe is misleading at best.
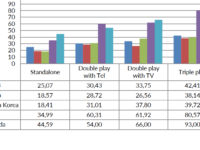
European Commission Backed Study Confirms Canada Among the Most Expensive for Broadband Internet Access
The European Commission has released a new study it commissioned on broadband pricing in Europe and several other leading countries. It confirms yet again what Canadian consumers have long suspected: Canada is among the most expensive countries in the developed economy world for broadband Internet services. The study, which provides data on the 2016 retail pricing for consumers throughout the EU, Canada, the U.S., Japan, South Korea, Norway, and Iceland, found Canadians consistently face some of the most expensive pricing regardless of speed or whether the packages include local telephone and television services. The survey was conducted over a two-week period in October 2016 and included retail pricing for five major Canadian ISPs: Bell, Shaw, Rogers, Videotron, and Telus. The data includes procedures to account for one-off fees and other discounts.
Canada – European Union Data Sharing Agreement Sent to EU Court of Justice for Review
Earlier this year, Canada and the European Union announced that they had reached agreement on sharing airline passenger name record data. The data shared includes names, addresses, and credit card numbers of airline passengers. The agreement was signed in June (video of the signing here), but approval from the European Parliament was required. In light of growing privacy concerns, that approval has proven more difficult to obtain than previously anticipated.
Rather than simply grant approval, the European Parliament has narrowly voted to send the agreement to the European Court of Justice for review to ensure that it is compliant with European law including EU treaties and the European Charter of Rights and Freedoms (the final vote was 383 to 271 with 47 abstentions). The resolution notes that the European Data Protection Supervisor (effectively the Privacy Commissioner for the EU) issued an opinion in September 2013 that questioned the necessity and proportionality of agreements to transfer passenger information between jurisdictions. The EDPS opinion features an extensive review of the agreement and raises pointed questions about specific provisions along with numerous recommendations for reform.
The decision means that the Canada – EU data sharing agreement will be delayed by at least one to three years while the court conducts its review. The review will raise several important privacy issues including the effectiveness of exchanging passenger information in combating terrorism and the state of Canadian privacy law. The European Court of Justice has already struck down the European Data Retention Directive, suggesting that this agreement could also face tough scrutiny.
Did Canada Cave on the Pharmaceutical Patent ISDS Issue in CETA?: Still No Text, But Official Comments Suggests It Did
For the second time in less than a year, Canada and the EU have announced that they reached agreement on the Canada – EU Trade Agreement. Back in October 2013, there was an announcement of an agreement “in principle”. The announcement did not include a release of the text and the parties said there was still further work to be done on drafting and legal analysis. Yesterday, brought another announcement of an agreement on the text. Once again, the announcement did not include a release of the text and the parties said there was still further work to be done on legal review and translation into 23 languages.
Given the agreement is 1,500 pages, the additional work is expected to take a considerable amount of time. While government ministers claimed that CETA “is ready for debate and ratification”, the reality is that there cannot be a meaningful, informed debate without the actual text. Releasing it for full study and comment is the essential next step.
Analysis without the text is difficult, however, the combination of prior leaks and media reports indicate that Canada caved on its concerns regarding the potential replication of Eli Lilly-style pharmaceutical patent lawsuits.