The Copyright Board of Canada has issued an order in the tariff proceedings with Access Copyright that indicates its preliminary view is that it will not support the collective’s demand for a provision that would require deletion of digital copies made under a copying tariff where an institution stops relying […]
Fair Dealing by Giulia Forsythe (CC BY-NC-SA 2.0) https://flic.kr/p/dRkXwP
Copyright
Appointment of New Copyright Board of Canada Chair Offers Chance for Change
Copyright Board of Canada chair William J. Vancise will see his term come to an end this month, opening the door for the government to start the process of reforming the much-criticized board. Vancise has served the maximum two terms as chair, with his time marked by the Supreme Court of Canada’s rejection of the board’s approach to fair dealing, ongoing frustration from stakeholders about board administrative processes, and the failure of the board to broaden its approach by becoming more inclusive of the public.
The exclusion of the public stands in sharp contrast to the CRTC and Competition Bureau, which have both taken steps in recent years to involve the public more directly in policy making activities, hearings, and other issues. By contrast, the Copyright Board does little to encourage public participation, despite the fact that its decision often have an impact that extends beyond the parties before it. When asked recently about the accessibility and participation concerns, the board pointed to an internal working group as evidence that it regularly reviews its practices and compared itself to the Federal Court of Appeal, noting that “of course they [the public] don’t participate, because they don’t really belong there, per se.”
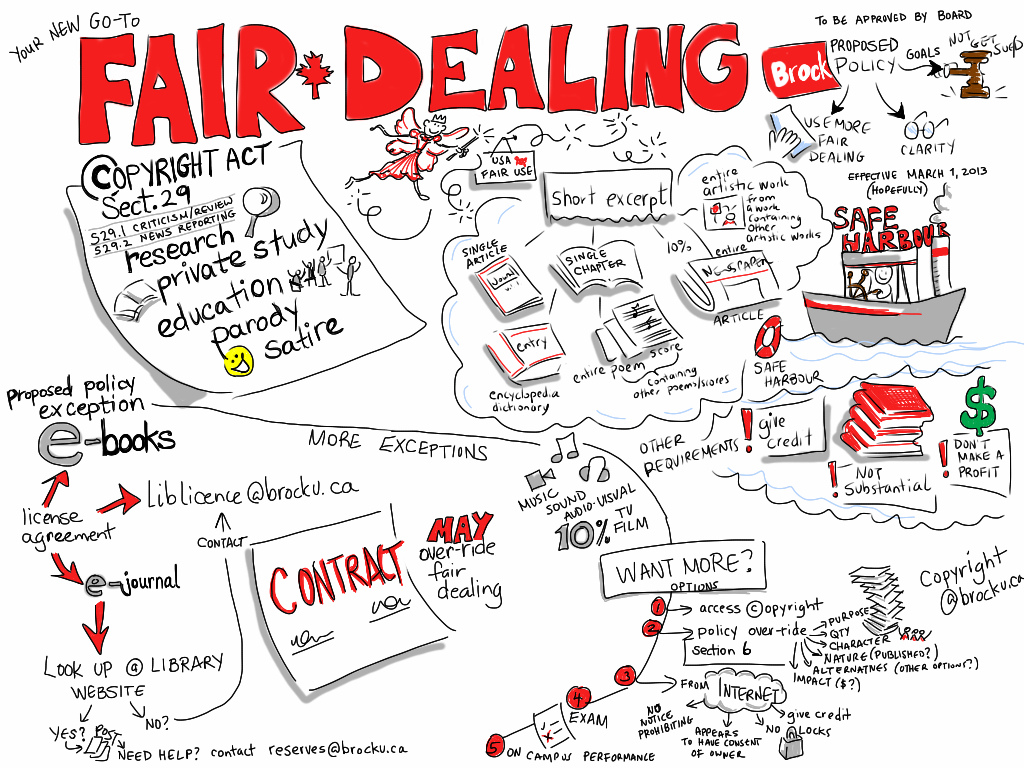
Access Copyright Urges Copyright Board to Ignore Bill C-11’s Expansion of Fair Dealing
As I noted in a post yesterday, Access Copyright has filed its response to the Copyright Board of Canada’s series of questions about fair dealing and education in the tariff proceedings involving Canadian post-secondary institutions. Yesterday’s post focused on how Access Copyright has urged the Copyright Board to ignore the Supreme Court of Canada’s ruling on the relevance of licences to a fair dealing analysis. Today’s post examines the collective’s response to the Copyright Board’s question on the effect of the fair dealing legislative change in Bill C-32/C-11. Access Copyright engages in revisionist history as it seeks to hide its extensive lobbying campaign that warned that the reforms would permit mass copying without compensation.
For two years during the debates over the bill, Access Copyright stood as the most vocal opponent of the expansion of the fair dealing purposes to include education. Given its frequent public comments and lobbying efforts on the bill, one would think its response to the Copyright Board, would be pretty straight-forward. For example, it created a copyright reform website – CopyrightGetitRight.ca – that warned:
the education exception will permit mass, industrial-scale copying (equivalent to millions of books every year) without compensation to the creators and publishers who invested their creativity, skill, money and effort to produce this content.
Access Copyright Urges Copyright Board to Ignore Supreme Court Ruling on Fair Dealing
Access Copyright has filed its response to the Copyright Board of Canada’s series of questions about fair dealing and education in the tariff proceedings involving Canadian post-secondary institutions. I have several posts planned about the 40 page response, which continues the copyright collective’s longstanding battle against fair dealing. This one focuses on Access Copyright’s astonishing effort to urge the Copyright Board to reject the Supreme Court of Canada’s clear ruling on the relevance of licensing within the context of fair dealing.
Access Copyright has frequently argued that the availability of a licence should trump fair dealing. For example, in the 2001 copyright consultation it stated:
As a rule, where collective licensing is in place there should be no exception or limitation to a right for which the holder has a legitimate interest. As defined in the Act, anytime that a licence to reproduce a work is available from a collective society within a reasonable time, for a reasonable price and with reasonable effort, it is commercially available.
Access Copyright reiterated its position in its 2003 intervention in the Law Society of Upper Canada v. CCH Canadian case. It argued:
U.S. Calls Out Canadian Data Protection as a Trade Barrier
The U.S. Trade Representative issued its annual Foreign Trade Barrier Report on Monday. In addition to identifying the geographical indications provisions in the Canada – EU Trade Agreement, telecom foreign ownership rules, and Canadian content regulations as barriers, the USTR discussed regulations on cross-border data flows. I wrote about the […]






